Augmented reality (AR) is an emerging technology and subsequent buzzword across multiple industries. The strength of AR is like no other when it comes to the manufacturing sector. Since the industry revolves around in-depth-employee training, product design and production as well logistics and maintenance, instant access to real-time data and graphics visualizations whilst remaining hands-free is a game-changer.
AR is a technology that superimposes a computer-generated image onto the users’ view of the real world. It can be delivered through a camera lens otherwise known as mobile AR, or through AR smartglasses and headsets which provide a more immersive experience of digital interaction. In effect, users can access an enhanced version of their world with access to information, video, graphics, and sound to complement their surroundings.
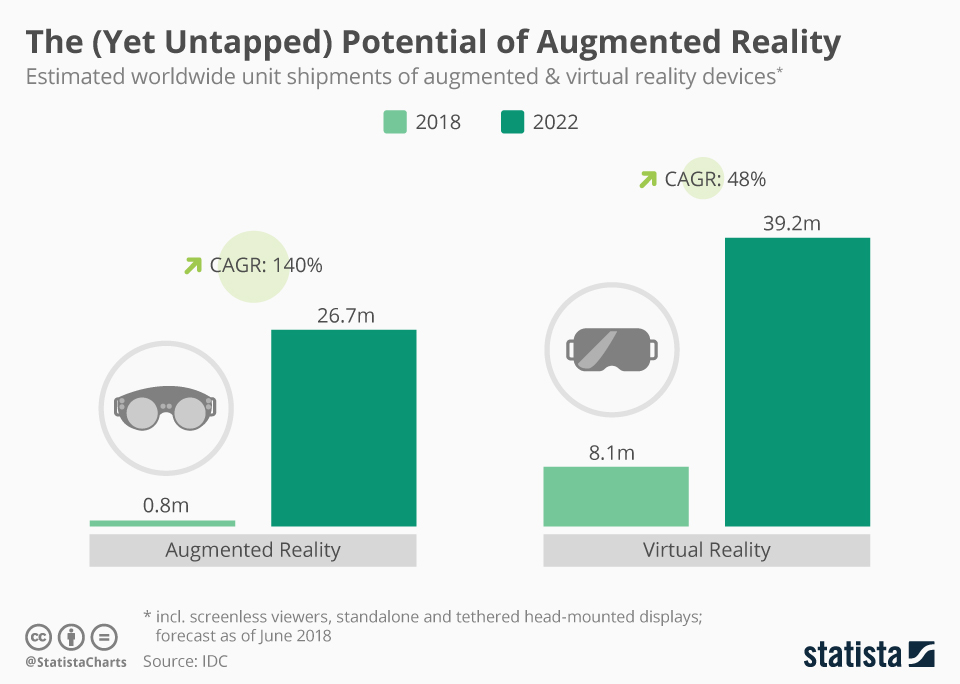
Potential of AR 2018 – 2022: (Statista)
Augmented reality is currently just beginning to emerge as a useful tool in the workplace. Its potential is vast and AR device shipments is forecast to increase more than 30-fold by the end of 2022.
What was once merely a sci-fi idea has become a reality with AR and has exploded with the ubiquity of mobile devices and powerful computer processes over the last decade. It’s relatively inexpensive and the initial investment is sure to pay for itself in the manufacturing sector; here’s how.
1. Access, store and manipulate data
Service engineers and manufacturers can easily go up to any item that’s supported with IoT technology and identify the object to help retrieve information from the company’s back-end enterprise resource planning system. As such, they will find access to the object’s specifications, location, inventory, and lead times. Gone are the days of writing specs down and storing such data on spreadsheets awaiting interpretation.
Manufacturing warehouse teams can use AR-enabled apps to scan QR codes, view live video feeds, graphics, and images to retrieve all the information they need on any given product. This is particularly useful for new team members and trainees who can then use their own initiative to repair machines by following instructions on their AR device, for instance.
2. Speed and accuracy
Consider the time and hassle it would traditionally take for fighter jet engineers to assemble an aircraft and the level of training that would go into doing so. With the help of AR smartglasses that utilize depth sensors, cameras, and motion sensors that superimpose images onto the view of real-life during these engineering sessions; they can see the digital rendering of bolts, cables, and parts that are complemented by information and instructions on how to assemble each component.
With this strategy, the accuracy of engineers can go up by 96% and increase the speed at which they work by up to 30%. What’s more, this isn’t exclusive to aircraft engineering. The manufacturing of all products can be elevated by speed and accuracy through AR-enabled devices that offer information and instructions on assembling, repairs and maintenance.
3. Access to factory floor: problems and procedures
Regardless of your specific market within the manufacturing industry, give your team access to the real-time happenings on the shop or factory floor. This should include information on parts, machinery, and stock, as well as the location of key team members within the company. AR has the capacity to relay this information onto a virtual map of the factory floor for employees to refer to when they need assistance.
In the event of safety, having instant hands-free access to information on hazards, no-go zones and safe escape routes is an effective and mostly, imperative way to keep your team safe in a potentially dangerous setting.
With AR in place, the entire manufacturing operations team can directly show maintenance and engineering teams the problems they incur as and when they happen. Sophisticated AR technology allows for the collaboration between teams on diagnosing the problems and resolving them without interfering with production.
4. Reduce production downtime
Businesses operating in the manufacturing industry heavily rely on minimizing downtime – that is the halt of operations due to machinery failure or disruptions. It can negatively impact profitability as well as the supply chains of their customers – potentially costing hundreds of thousands of pounds.
With the help of augmented reality technology, a manufacturing team can quickly identify and prevent downtime from ever occurring. Should a machinery failure occur; the time it takes to collaboratively resolve the issue is minimized through real-time information from off-site technicians who can talk engineers through the repair process.
Honing in on AR apps on mobile devices, employees have an actionable way to immediately and effectively resolve the issues they incur there and then; without having to rely on management teams. Operations become more seamless and production continues.
5. AR training in the manufacturing setting
Both VR and AR have demonstrated great potential when it comes to training employees. However, augmented reality certainly has the upper hand when it comes to training in the manufacturing sector.
To begin with, virtual reality is a truly immersive environment that doesn’t allow its users the flexibility of dipping in and out of the real world. Secondly, it requires fairly large hardware for a truly interactive experience. Whilst this is great across many other training settings; those working in manufacturing will need to enjoy a hands-free training session where they are more than aware of their real-life (and sometimes dangerous) settings. Mesmerise VR Training allows employers to reuse modules to instil consistent skills and competencies across their workforce.
Augmented reality training in manufacturing can allow trainees access to digital machinery supplemented with overlaid information about each part and how to operate it. In any event, whether that’s operating the machinery, replacing it, moving it, or repairing it; the processes to do so can be shown in video, step-by-step instructions, and under the supervision of specialist technicians that can guide trainees through certain procedures.
